Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (115), p.43 - 49, 2023/04
Oxidation and dissolution of uranium oxide materials has been a subject of numerous studies as a basis of the geological disposal technology for spent nuclear fuel. The understandings obtained by these studies provide useful suggestions for research and development regarding the retrieval and storage of nuclear fuel debris generated by a nuclear severe accident. Here, these research backgrounds of oxidative dissolution of uranium oxides are briefly reviewed and some studies relating to radiation-induced reactions will be introduced.
 O
O -induced oxidative degradation of simulated fuel debris
-induced oxidative degradation of simulated fuel debrisKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (113), p.61 - 64, 2022/04
The severe accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station resulted in generation of fuel debris. The fuel debris is in contact with water and the radiolysis of water can accelerate degradation of the debris. The analysis of particles sampled from inside or near the damaged reactors indicates the complicated compositions of the fuel debris. It is challenging to estimate the effect of water radiolysis on such a complicated material. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the potential degradation process by leaching experiments of simulated fuel debris in aqueous H O
O solution. The results show that the reaction of H
solution. The results show that the reaction of H O
O induced uranium dissolution from most of the samples and then formation of uranyl peroxides. In contrast, a sample that had U-Zr oxide solid solution as the major phase exhibited remarkable resistance to H
induced uranium dissolution from most of the samples and then formation of uranyl peroxides. In contrast, a sample that had U-Zr oxide solid solution as the major phase exhibited remarkable resistance to H O
O . These findings revealed that the degradation of the simulated debris reflects the reactivity and stability of the uranium phase in the matrices.
. These findings revealed that the degradation of the simulated debris reflects the reactivity and stability of the uranium phase in the matrices.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (112), p.15 - 20, 2021/11
Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo code enabling radiation kinetics, which is often used in diverse research fields, such as atomic energy, engineering, medicine and science. After released in 2010, the PHITS code has been developed to expand its functions and to improve its convenience. In the few years, track-structure mode has been introduced in PHITS that can simulate each atomic interaction by electrons, positions, protons and carbon ions in liquid water. Thanks to the development of track-structure mode, the latest PHITS code enables microscopic dose calculations by decomposing it to the scale of DNA. Aiming at realizing the track-structure mode with high precision, the further developments of electron and ion track-structure mode for arbitrary materials are recently ongoing. This review shows the development history and future prospect of PHITS track-structure mode, which can expect to be further applied to the research fields of atomic physics, radiation chemistry, and quantum life science.
Miyazaki, Yasunori; Sano, Yuichi
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (112), p.27 - 32, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (110), p.13 - 19, 2020/10
The article depicts how to estimate the external exposure dose for wild animals using electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. The relationship between the CO radical intensity and the absorbed dose, that is, dose response curve of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed, and the detection limit of our method was estimated. The estimated detection limit of 33.5 mGy is comparable to the previously reported detection limit for human molar teeth. The external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined using this dose response curve. The estimated external exposure dose were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
radical intensity and the absorbed dose, that is, dose response curve of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed, and the detection limit of our method was estimated. The estimated detection limit of 33.5 mGy is comparable to the previously reported detection limit for human molar teeth. The external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined using this dose response curve. The estimated external exposure dose were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
Tanaka, Kiriha*; Muto, Jun*; Nagahama, Hiroyuki*; Oka, Toshitaka
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (110), p.21 - 30, 2020/10
In a fault dating by electron spin resonance (ESR), the number of unpaired electrons trapped in defects in minerals contained in a fault material is detected as ESR intensity. Based on the quantitative change of the intensity before and after an earthquake, the last age of a fault movement can be estimated. However, this method has a hypothesis called "zero-setting" which assumes the decrease in the ESR intensity to zero by fault movement during an earthquake. In order to understand and demonstrate zero-setting, the analysis of the natural fault materials and experiments mimicking fault movements have been conducted. In this paper, we summarized the previous studies about zero-setting by fault movement and described the current status and challenges.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (108), p.11 - 17, 2019/11
Scintillators are generally used to detect various kinds of particles such as electrons, gammas, protons and heavy ions. Scintillators emit photons according to the energy deposited to the crystal. It is also known that light yield is suppressed for particles depositing energy densely owing to quenching. Moreover, it is suggested that quenching is attributed to transfer of energy from excited fluorescent molecules to damaged molecules (F rster mechanism or Dexter mechanism). In this study, energy deposition in a scintillator crystal by radiation was calculated using radiation transport codes to finally obtain excitation and damage of fluorescent molecules. Based on the calculation, spatial configuration of exited and damaged molecules. Then the probability that F
rster mechanism or Dexter mechanism). In this study, energy deposition in a scintillator crystal by radiation was calculated using radiation transport codes to finally obtain excitation and damage of fluorescent molecules. Based on the calculation, spatial configuration of exited and damaged molecules. Then the probability that F rster mechanism takes place in excited molecules were estimated to obtain the number of fluorescent molecules that emit photons. As a result, light yield is proportionally increased with increase in the incident energy in case of electron incidence. On the other hand, light yield is increased non-linearly in case of proton incidence. This trend is in a good agreement with the experimental results.
rster mechanism takes place in excited molecules were estimated to obtain the number of fluorescent molecules that emit photons. As a result, light yield is proportionally increased with increase in the incident energy in case of electron incidence. On the other hand, light yield is increased non-linearly in case of proton incidence. This trend is in a good agreement with the experimental results.
 O
O concentration on oxidative dissolution of U
concentration on oxidative dissolution of U O
OKumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (107), p.77 - 78, 2019/04
Reaction of hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) with uranium dioxide (UO
) with uranium dioxide (UO ) oxidizes U(IV) to water-soluble U(VI). In the concept of direct geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel, this reaction is expected to induce dissolution of UO
) oxidizes U(IV) to water-soluble U(VI). In the concept of direct geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel, this reaction is expected to induce dissolution of UO matrix of the spent fuel. This study investigate effect of H
matrix of the spent fuel. This study investigate effect of H O
O concentration on the kinetics and the yield of U(VI) dissolution of this reaction. A series of experiments of the reaction of H
concentration on the kinetics and the yield of U(VI) dissolution of this reaction. A series of experiments of the reaction of H O
O with UO
with UO powder dispersed in water has been carried out. The experimental results reveal that increase in the H
powder dispersed in water has been carried out. The experimental results reveal that increase in the H O
O concentration slows down the reaction and decreases the yield of U(VI) dissolution. This observation suggests that a reaction intermediate is generated in the course of the H
concentration slows down the reaction and decreases the yield of U(VI) dissolution. This observation suggests that a reaction intermediate is generated in the course of the H O
O reaction on the surface of UO
reaction on the surface of UO .
.
Kai, Takeshi; Yokoya, Akinari*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Watanabe, Ritsuko*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (106), p.21 - 29, 2018/11
It is thought to that the biological effects such as cell death or mutation are induced by complex DNA damage which are formed by several damage sites within a few nm. As the prediction of complex DNA damage at an electron track end, we report our outcomes. These results indicate that DNA damage sites comprising multiple nucleobase lesions with a single strand breaks can be formed by multiple collisions of the electrons within 1 nm. This multiple damage site cannot be processed by base excision repair enzymes. Pre-hydrated electrons can also be produced resulting in an additional base lesion over a few nm from the multi-damage site. This clustered damage site may be finally converted into a double strand break. These DSBs include another base lesion(s) at their termini that escape from the base excision process and which may result in biological effect. Our simulation is useful to reveal phenomena involved in radiation physico-chemistry as well as the DNA damage prediction.
Kitamura, Akane; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (104), p.29 - 34, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Lin, M.*; Yokoya, Akinari*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (103), p.29 - 34, 2017/04
Reactivity of edaravone (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one), which is known to show high antioxidative properties, with oxidative species, such as hydroxyl radical (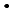 OH) and azide radical (N
OH) and azide radical (N
 ), was investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment, and generation behavior of edaravone radicals produced through these reactions were observed. It was shown that OH-adducts are produced by the reaction with
), was investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment, and generation behavior of edaravone radicals produced through these reactions were observed. It was shown that OH-adducts are produced by the reaction with 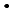 OH in contrast to the other oxidative radicals, which react with edaravone by an electron transfer reaction. Chemical repair properties of edaravone against DNA lesions produced by reactions of DNA with oxidative species were also investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment with deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) and a
OH in contrast to the other oxidative radicals, which react with edaravone by an electron transfer reaction. Chemical repair properties of edaravone against DNA lesions produced by reactions of DNA with oxidative species were also investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment with deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) and a  -radiolysis experiment with plasmid DNA solutions. It was observed that edaravone reduced dGMP radicals just after produced in a dilute aqueous solution and inhibited some base lesions on plasmid DNA more effectively than single strand breaks. These results show that edaravone may protect living system from oxidative stress, such as radiation, by not only scavenging oxidative species but also reducing precursors of DNA leisons.
-radiolysis experiment with plasmid DNA solutions. It was observed that edaravone reduced dGMP radicals just after produced in a dilute aqueous solution and inhibited some base lesions on plasmid DNA more effectively than single strand breaks. These results show that edaravone may protect living system from oxidative stress, such as radiation, by not only scavenging oxidative species but also reducing precursors of DNA leisons.
Hata, Kuniki
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (103), P. 65, 2017/04
no abstracts in English
Kai, Takeshi; Yokoya, Akinari; Fujii, Kentaro; Watanabe, Ritsuko
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (101), p.3 - 11, 2016/04
Behavior analysis of low energy electrons in liquid water provides the fundamentals for successive radiation chemistry, and it makes analysis of DNA damage implication involved in the electrons possible. We have progressed theoretical studies for radiation physicochemical process of liquid water to clear the role of low-energy secondary electrons damage to DNA. The process has included many unknown factors for the DNA damage so far. Based on the results, we implied a newly formation process of unrepair DNA damage produced by the secondary electrons assumed that it was ejected from DNA by impact of a high energy electron. We report our outcomes separately in three manuscripts entitled "Recent progress of radiation physicochemical process (first, second, third parts)" to journal of radiation chemistry. In this first part, we outline recent status of studies for the DNA damage and the radiation physicochemical process, we also show calculation method of electron impact cross sections involved strongly in electron deceleration in liquid water in the topics of our outcomes. From the calculated results, we also report our prediction, which are different from previous one, for electron thermalization.
Kai, Takeshi; Yokoya, Akinari*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Watanabe, Ritsuko*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (102), p.49 - 56, 2016/00
Behavior analysis of low energy electrons in liquid water provides the fundamentals for successive radiation chemistry, and it makes analysis of DNA damage implication involved in the electrons possible. We have progressed theoretical studies for radiation physicochemical process of water to clear the role of secondary electrons damage to DNA. The process has included many unknown factors for the DNA damage so far. We implied a newly formation process of unrepair DNA damage produced by the secondary electrons. We report our outcomes separately in three manuscripts entitled "Recent progress of radiation physicochemical process (first, second, third parts)". In this second part, we show calculated results of thermalization lengths and times of electrons in water to verify a dynamic Monte Carlo code developed in this study. From the calculated results, we also report our prediction, which are different from previous one, for thermalization and pre-hydration processes.
Kurashima, Satoshi
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (100), p.49 - 51, 2015/10
no abstracts in English
Tamada, Masao
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (100), P. 16, 2015/10
Collection of a rare metal form hot spring water attracted medias and had a public response by reports of numerous newspapers and television programs in my 35 years' research and development of radiation processing technologies and its technology management. Collection experiments of the rare metal were carried out in Kusatsu Onsen, Gunma prefecture, where discharge of hot spring water is the largest in Japan. We were on standby 6 am there when morning live broadcast started from 8 am. The invention of emersion grafting solved the problems in the cost reduction of adsorbent production owing to its high grafting yield and led the way for technology transfer of filter for the removal of metal ions in ppb level from semiconductor cleaning liquid and adsorbent for radio-active cesium.
Hase, Yoshihiro
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (100), p.86 - 88, 2015/10
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation in zeolite/water mixtures
-ray irradiation in zeolite/water mixturesKumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (99), p.53 - 56, 2015/04
Radiation-induced degradation of 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh) in zeolite/water mixtures was studied in order to consider a possibility of adsorption on zeolites to improve efficiencies of irradiation treatments of water contaminated by organic compounds. The degradation of 2-ClPh by  -ray irradiation was investigated as a model compound. The degradation was evaluated by chloride ion (Cl
-ray irradiation was investigated as a model compound. The degradation was evaluated by chloride ion (Cl ) production. A high concentration of Cl
) production. A high concentration of Cl was observed after the irradiation of a mixture with a mordenite-type zeolite (NaMOR), whereas A-type and X-type zeolites showed no significant effect. Therefore, for the mixture with NaMOR, effects of pH of the solution and of the 2-ClPh concentration were examined. At pH 5.7, the excess production of Cl
was observed after the irradiation of a mixture with a mordenite-type zeolite (NaMOR), whereas A-type and X-type zeolites showed no significant effect. Therefore, for the mixture with NaMOR, effects of pH of the solution and of the 2-ClPh concentration were examined. At pH 5.7, the excess production of Cl was induced by the addition of NaMOR. Concurrently, adsorption of 2-ClPh on NaMOR was observed. When the mixture contained a higher concentration of 2-ClPh at pH 5.7, the Cl
was induced by the addition of NaMOR. Concurrently, adsorption of 2-ClPh on NaMOR was observed. When the mixture contained a higher concentration of 2-ClPh at pH 5.7, the Cl production increased. The adsorption of 2-ClPh also increased with increasing concentration. The results suggest that organics adsorbed on zeolites are decomposed by irradiation effectively at high adsorption concentrations.
production increased. The adsorption of 2-ClPh also increased with increasing concentration. The results suggest that organics adsorbed on zeolites are decomposed by irradiation effectively at high adsorption concentrations.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (97), p.13 - 27, 2014/00
Since the first observation of the energetic protons from the interaction between the short pulse high intensity laser and the thin-foil target, extensive studies have been carried out for more than 15 years. In the early period, the laser energy of kilo joule level is necessary to accelerate the protons more than 50 MeV. Such a large amount of laser energy is supplied only by a huge laser system, which typically is unable to make repetitive operation. However, thanks to the progresses in the laser technology, protons having the energies almost 50 MeV are successfully accelerated by the laser system with only less than 10 J of energy and with the capability of repetitive operation. These facts really show the advance of the laser-driven ion acceleration towards the possible fields of applications. Here in this paper the characteristics, the mechanisms and the recent experimental results of the laser-driven proton acceleration are shown.
Tamada, Masao
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (96), P. 1, 2013/09
Innovations in scientific technology are expected to revive the Japanese economy. Advantages of quantum beam technology are to be able to develop materials which have novel properties and superior functionality to those achieved by chemical methods. Such materials are favorable for technology transfer since they have higher potential than conventional products. This point is advantageous in quantum beam technology. Hence, it is extremely important that research and development of both new technology of quantum beams and new seeds aiming at industrial applications.